The Truth about Pesticides: Chemical Warfare on All Bodies of Life
"Just like air - the soil does not care if it is polluted. But we humans do care - because if it is polluted, it can no longer provide all the services we depend on. So, we have to be the ones taking care of it."
- Alfred Grand, Organic Farmer and Entrepreneur

Farmers know that soil matters. But there is a great disconnect between farmers and the rest of the world – especially consumers and researchers.
The health of our soils affects all aspects of life on Earth, from the various organisms living within it to how resilient we are in the face of climate change. In fact, one gram can hold over a billion bacteria – many still undiscovered! These microscopic creatures help us develop antibiotics and other medicines that keep us healthy.
That's something to really think about when considering soil for its role in absorbing and purifying water available for humans' consumption or regulating excess rainfall during floods - which have become more erratic due to global warming. Soil truly is essential; caring about this precious resource means making sure future generations continue having access its benefits as well, thus everyone should be talking about protecting our earthy foundation!
“Soil is life, so caring about soil means caring about life.”
- Anna Zampa, Project Specialist, 100Million Farmers
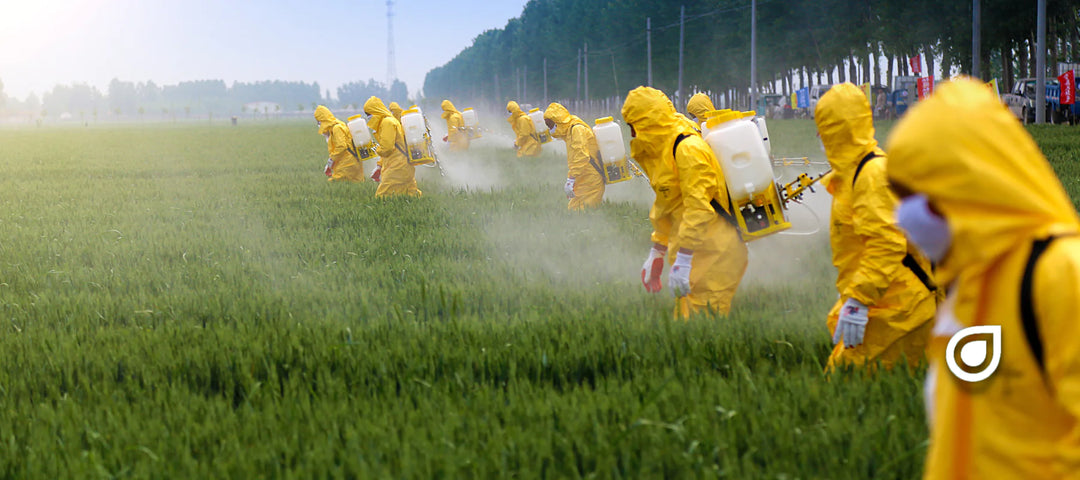
Are Pesticides a Necessary Evil? Or Are They Actually Chemical Warfare Against All Bodies of Life?

Pesticides are one of the significant contributors to environmental pollution, which helped create the environmental movement of the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Pesticides are killing off our core microbes. In the past 30 years, pesticides have reduced nature's bacteria and fungi by more than 99%, primarily due to pesticides running rampant and killing anything that moves (or doesn't move).
Pesticides can also harm beneficial insects and animals, disrupt ecosystems, and lead to the development of pesticide-resistant pests.
Pesticides contribute to various adverse health outcomes, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, congenital disabilities, reproductive failures, developmental abnormalities, and learning disabilities.
Short-term exposure to high levels of pesticides can cause symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and nausea.
Long-term exposure to pesticides has been linked to an increased risk of certain cancers and neurological and reproductive effects.
Which Countries are the Top Producers of Pesticides?

(Source: https://www.worldometers.info/food-agriculture/pesticides-by-country)
Brutal Truths About the Negative Impact of Overexposure to Pesticides
Pesticides induce oxidative DNA damage, adducts, and single or double-strand DNA breaks. Various mechanisms of DNA repair deal with such damages and help maintain cell integrity. Alteration in DNA repair genes modulates the individual's susceptibility toward DNA repair and multiple diseases.

(Source: Ledda, C., Cannizzaro, E., Cinà, D. et al. Oxidative stress and DNA damage in agricultural workers after exposure to pesticides. J Occup Med Toxicol 16, 1 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12995-020-00290-z)
Pesticide exposure is a risk factor for cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.

(Source: Kaur K, Kaur R. Occupational Pesticide Exposure, Impaired DNA Repair, and Diseases. Indian J Occup Environ Med. 2018 May-Aug;22(2):74-81. doi: 10.4103/ijoem.IJOEM_45_18. PMID: 30319227; PMCID: PMC6176703)
What are some Chemicals used in Pesticides Linked to Cancer?
Three chemicals used as pesticides – arsenic, ethylene oxide, and lindane – are among agents rated as group one carcinogens, or conclusive causes of cancer, by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), as is the chemical 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), which may occur as a contaminant in certain pesticides.
How many types of Pesticides are there?
There are many different types of pesticides. One common way to classify pesticides is based on their mode of action or how they kill or control pests.
Some common types of pesticides include:
1. Insecticides: These pesticides are used to control insects and other arthropods. They can be further classified as contact, stomach, or systemic insecticides.
2. Herbicides: These pesticides are used to control weeds and other unwanted plants. They can be further classified as selective or non-selective herbicides.
3. Fungicides: These pesticides are used to control fungal diseases in plants. They can be further classified as protectant or systemic fungicides.
4. Rodenticides: These pesticides are used to control rodent pests such as rats and mice. They can be further classified as anticoagulants, acute toxins or growth regulators.
5. Molluscicides: These pesticides are used to control mollusk pests such as snails and slugs.
6. Bactericides: These pesticides are used to control bacterial diseases in plants and animals.
7. Miticides: These pesticides are used to control mites and other arthropod pests.
8. Nematicides: These pesticides are used to control nematode pests.
It's important to note that some pesticides can be multi-purpose and target several types of pests, and some can have multiple modes of action. Also, new types of pesticides are being developed, such as biopesticides derived from natural materials such as microorganisms. They are considered less harmful to human health and the environment.
How do Pesticides get into Our Water Supply?
Pesticides can enter the water supply through a variety of means.
One way is through runoff, rain or irrigation water carries pesticides from treated fields or lawns into nearby waterways.
Pesticides can also leach into groundwater from soil treated with chemicals.
Additionally, pesticides can enter the water supply through agricultural or residential drainage systems or improper storage or disposal of pesticides.

Climate change also plays a role as the increasing frequency of extreme weather events such as heavy rainfall or floods can flush pesticides into streams and rivers, carrying them into larger bodies of water and even into the groundwater.

What are some common symptoms of pesticide toxicity in the human body to be aware of?
Pesticide toxicity can cause a wide range of symptoms depending on the type of pesticide, the amount of exposure, and the duration of exposure.
Some common symptoms of pesticide toxicity in the human body include:
1. Acute symptoms: Headaches, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue are common symptoms of acute pesticide exposure. Exposure can lead to seizures, unconsciousness, and even death in severe cases.

2. Skin irritation: Pesticides can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions, including rashes, itching, and burning sensations.

3. Respiratory symptoms: Pesticides can cause respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing.
4. Eye irritation: Pesticides can cause eye irritation, redness, and watering.

5. Neurological symptoms: Pesticides can cause neurological symptoms such as tremors, confusion, memory loss, and depression.
6. Endocrine disruption: Pesticides can disrupt the body's endocrine system, leading to changes in hormone levels and symptoms such as infertility, birth defects, and developmental delays.

It's important to note that some symptoms may not appear immediately after exposure and may take days or weeks to manifest. Some long-term health effects of pesticide exposure may only appear years after the exposure.
It's also important to remember that the symptoms can vary depending on the type of pesticide, the dose, the duration of exposure, and the health status of the person exposed.
If you suspect you have been exposed to pesticides, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately and inform the health care provider of the exposure.
What is the human body's first line of defense against the toxic chemicals within pesticides?
The skin and mucous membranes are the human body's first line of defense against toxic chemicals, including those found in pesticides.
These physical barriers prevent many harmful substances from entering the body.
The skin is a barrier to protect the body from harmful substances and infection. At the same time, mucous membranes in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts also help to filter out toxic substances.
Additionally, enzymes in the liver and other organs detoxify and neutralize harmful chemicals, such as pesticides, that may enter the body.

Other mechanisms, such as the immune system, protect the body against harmful chemicals by identifying and neutralizing foreign substances.
However, these mechanisms are not specific to pesticides, and they are not a primary defense against chemical toxicity but rather a secondary instrument that is activated after exposure.
It's important to note that these defenses can be overwhelmed if the exposure is very high, prolonged, or repeated, leading to significant health impacts.
What can we do proactively to take better care of our Microbiome or Gut Flora to help keep us healthy amidst fighting off the toxic chemicals in these pesticides?

There are several ways to take care of our microbiome and gut flora to help keep us healthy amidst fighting off the toxic chemicals found in pesticides:

1. A diverse and balanced diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods, such as yogurt and kefir, can help to promote a healthy and diverse microbiome.

2. Avoiding antibiotics and other drugs: Antibiotics and other medications can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, so it is essential to use them only when necessary.
3. Reducing stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiome, so it is crucial to find ways to manage stress through more mindful physical activities. Such as yoga, meditation, walking, and stretching -- any exercise that puts you in a positive state of mind should be a mandatory part of the daily protocol.
4. Minimizing exposure to pesticides and other toxins: Avoiding exposure to pesticides and other toxins can help to keep the gut microbiome healthy. This means eating organic food, using natural cleaning products, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.

5. Probiotics and prebiotics: Consuming probiotics, which are live microorganisms that can provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts, and prebiotics, which are non-digestible food ingredients that stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, can help to maintain a healthy gut microbiome.

It's important to note that maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is a complex process.

It's not only about avoiding exposure to toxins but also about a combination of lifestyle, diet, and other factors that can positively impact the gut microbiome.
Are any minerals, nutrients, or vitamins known to positively impact the human body's natural detoxification process of excretion?
Several minerals, nutrients, and vitamins are known to positively impact the human body's natural detoxification process of excretion.
Some of these include:
1. Fiber: Eating a diet high in fiber can help to promote regular bowel movements and flush toxins out of the body.
2. Vitamin C: This nutrient acts as an antioxidant and helps to neutralize free radicals, which can damage cells and contribute to chronic disease. Vitamin C also helps the body to produce glutathione, a compound that plays an essential role in detoxification.
3. Vitamin A: This nutrient is essential for maintaining the skin and mucous membrane, which act as the body's first line of defense against toxins.
4. Vitamin E: This nutrient acts as an antioxidant and helps to protect cells from damage.
5. Vitamin B12: This nutrient plays a vital role in producing red blood cells and maintaining the nervous system. It also helps in the metabolism of homocysteine, an amino acid that can be toxic when it builds up in the body.
6. Iron: This mineral is essential for producing hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. It also helps in the metabolism of some toxins.
7. Zinc: This mineral plays an essential role in the immune system and helps to neutralize toxins.
8. Selenium: This mineral acts as an antioxidant and helps to neutralize free radicals.
9. Magnesium: This mineral helps in the functioning of the nervous system and muscle and it also helps in the elimination of toxins through the kidneys and bowels.
10. Glutathione: This compound is a powerful antioxidant produced by the body and plays an important role in detoxification.

It's important to note that maintaining a balanced and healthy diet is essential for overall health, including the support of the body's detoxification process.
Also, taking supplements of these nutrients may only be appropriate for some; if you have a go-to holistic, integrated healthcare professional who is more familiar with your situation - before starting any supplement regimen.
We highlight our ELECTROLYTE BALANCE® product when it comes to ideal immune system function, overall health, and wellness.

Magnesium is an essential mineral critical in the body's natural detoxification process. Proper magnesium levels are vital for several reasons:
1. Enzyme function: Magnesium is necessary to properly operate over 300 enzymes in the body, including those involved in detoxifying harmful chemicals. Enzymes catalyze reactions that break down toxins and help to eliminate them from the body.
2. Glutathione production: Magnesium is essential for producing glutathione, an important antioxidant and detoxifying agent that helps neutralize free radicals and toxins in the body.
3. Supporting the liver: Magnesium is vital for the proper functioning of the liver, which is the body's primary detoxifying organ. Adequate magnesium intake supports the liver's ability to filter toxins and remove them from the body.
4. Helping eliminate toxins through the kidneys: Magnesium is necessary for the proper functioning of the kidneys, which help filter toxins and waste products out of the blood and excrete them in the urine.
5. Promoting regular bowel movements: Magnesium can help regulate bowel movements and eliminate toxins through the feces.
6. Regulating body temperature: Magnesium helps regulate body temperature by dissipating heat through sweat and helps in the excretion of toxins through sweat.

It's important to note that low magnesium levels can cause several health issues, such as muscle cramps, fatigue, and constipation. These symptoms can make it harder for the body to detoxify, so it's crucial to maintain adequate magnesium levels through a balanced diet and supplements if needed.

What role does water play in assisting the human body's natural detoxification process?
Water plays an essential role in assisting with the human body's natural detoxification process in a few ways:
1. Flushing toxins: Water helps to flush toxins out of the body by carrying them away in urine and sweat. Adequate water intake is essential to ensure that the kidneys and liver can function properly and effectively remove waste products and toxins from the body.
2. Enhancing digestion: Water is also essential for proper functioning of the digestive system. It helps to soften stools and move food through the intestines, which can assist in the elimination of toxins from the body.
3. Supporting the skin: Water is vital for the skin's overall health, one of the body's primary detoxification organs. Adequate water intake helps keep the skin hydrated and supports the elimination of toxins through sweat.
4. Regulating body temperature: Water helps to regulate body temperature by dissipating heat through sweat. Sweating can also help to eliminate toxins through the skin.
5. Aiding in the production of lymph: Drinking enough water is essential to help the lymphatic system function properly. Lymph is a fluid that circulates throughout the body and carries waste products and toxins away from the cells to be eliminated by the body.
It's important to note that the human body needs a sufficient amount of water intake; the recommended intake varies depending on factors such as age, sex, weight, and activity level.
Still, a general guideline is around eight glasses a day.

Dehydration can negatively affect the body's ability to detoxify and remove toxins, so it's essential to drink enough water to stay hydrated.
All in all, we must be aware of pesticides' implications on our environment and bodies.
The dangers of these toxic chemicals are far too great to ignore, as they can be both destructive and dangerous. We must stay informed of their properties and any potential health risks they may pose for us.

Additionally, education about the existence of different types of pesticides found commonly in food and water supplies must also be increased so that we can reduce the risk of contamination.
Furthermore, arming ourselves with knowledge about what steps we can take proactively to protect ourselves from toxins in pesticide exposure can do wonders for our overall well-being.
A healthy microbiome or gut flora is critical in helping us combat these dangerous chemicals, so maintaining a diet rich in minerals, nutrients, and vitamins could prove helpful.
Lastly, remember that staying hydrated is vital in helping our body detoxify itself. Awareness is half the battle in this fight against pesticides; proactive solutions and personal responsibility will always be necessary if we want to keep the environment clean and safe for generations.